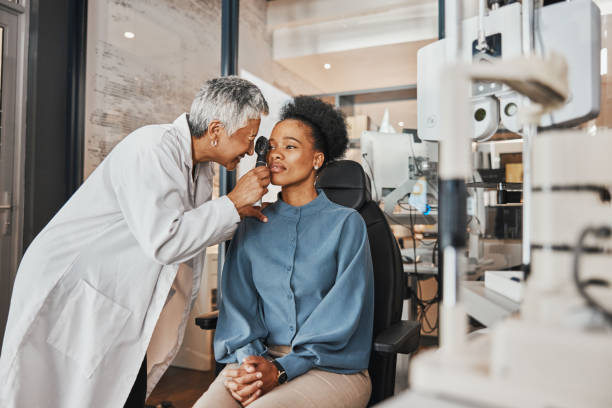
A comprehensive eye exam is more than just determining whether you need glasses or contact lenses. It’s a thorough evaluation of your overall eye health, designed to detect early signs of vision problems and other health conditions.
This is one of the most common eye tests conducted during an exam.
Refraction testing determines whether you need prescription lenses for refractive errors like:
– Myopia (nearsightedness)
– Hyperopia (farsightedness)
– Astigmatism
– Presbyopia
– Cornea
– Lens
– Iris
Your doctor may use dilating drops to get a clearer view.
This test checks for glaucoma by measuring the pressure inside your eyes (intraocular pressure). Glaucoma can lead to irreversible vision loss if untreated.
Types include: | Type | Description | |———————-|———————————————–| | Non-contact tonometry | Uses a puff of air to measure pressure | | Applanation tonometry | Directly gauges pressure using special tools |
You may be asked to press buttons when lights appear in various areas within your visual field.
Color vision tests screen for deficiencies in distinguishing colors, particularly useful in identifying color blindness or other retinal conditions affecting color perception.
Example task: Identifying numbers within patterns of colored dots (Ishihara test).
Depth perception evaluates how well both eyes work together to judge distance and three-dimensional space—essential for day-to-day activities like driving or sports.
Common method: Viewing objects through special lenses to determine alignment accuracy between both eyes.
Regularly undergoing these essential tests not only ensures that corrective measures for refractive errors are taken but also helps detect serious health concerns early on, such as diabetes, hypertension, or neurological disorders that may manifest through ocular symptoms. Prioritizing routine comprehensive exams is key to preserving long-term visual health and overall well-being.
How a Houston TX eye doctor conducts eye exams to assess your vision health
These exams are not merely for determining whether you need glasses or contact lenses—they are essential for detecting potential eye conditions and systemic health issues that may manifest in the eyes.
Key Services at an Eye Clinic in Houston TX
A comprehensive eye exam generally includes several tests and assessments designed to evaluate different aspects of vision and eye health.
- Discussion about your general health
- Current medications, if any
- Family history of eye diseases or conditions
- The Snellen chart is used to measure how clearly you see at various distances.
- Helps identify refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (farsightedness).
- Determines your exact lens prescription for glasses or contact lenses.
- Performed using a phoropter to measure how light rays bend as they pass through your eyes.
- Evaluates how well your eyes work together as a team. Issues here may indicate strabismus (crossed eyes) or other muscular problems.
- Assesses side vision to detect issues like glaucoma, which often affects peripheral vision first.
- A critical test for diagnosing glaucoma by measuring intraocular pressure. Non-contact tonometry involves a quick puff of air onto the eye, while applanation tonometry uses a small probe to gently touch the surface of the eye.
Importance of Detecting Eye Diseases Early
- Glaucoma– Often called the “silent thief of sight,” it can cause irreversible damage before noticeable symptoms appear.
- Cataracts– Clouding of the lens can lead to reduced vision over time.
- Macular Degeneration– Particularly common among older adults, this condition impacts central vision.
- Diabetic Retinopathy– A complication from diabetes that affects retinal blood vessels.
Systemic Health Conditions Revealed During Eye Exams
| Condition | Eye Exam Indicators |
| Diabetes | Swelling or bleeding in retinal blood vessels |
| Hypertension | Damage to blood vessels in the retina |
| Autoimmune Diseases | Inflammation inside the eye |
| High Cholesterol | Fatty deposits on corneal surfaces |
When Should You Schedule an Exam?
- Adults (18–60):Every two years if no symptoms are present; annually if at risk for conditions like diabetes or family history of glaucoma.
- Children:First comprehensive test at six months old, then at age three, followed by annual exams after school starts.
- Seniors (65+):Annual exams due to increased risk of cataracts, macular degeneration, and other age-related changes.
By addressing both preventive care and specific concerns during these exams, patients benefit from better management of their long-term ocular wellness while also gaining insights into overall health indicators observable through their eyes alone.
How a Houston TX optometrist can help maintain optimal vision through regular eye exams
Regular eye exams play a critical role in maintaining not only your vision but also your overall eye health. Many eye-related conditions develop gradually and may not present noticeable symptoms until they have progressed significantly. By scheduling routine exams, you can identify potential issues early and ensure that your eyes remain in optimal condition. Here’s a closer look at why these exams are essential.
Early Detection of Eye Diseases
Eye diseases such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy often progress silently without immediate signs or symptoms. A comprehensive eye exam can help detect these conditions before they cause irreversible damage to your vision.
- Glaucoma: Often referred to as the “silent thief of sight,” this condition can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated.
- Macular Degeneration: Regular monitoring is crucial for identifying this age-related issue that affects central vision.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Individuals with diabetes are at higher risk for retinal damage, which can be detected early through routine screening.
Vision Correction and Updates
As we age or undergo life changes, our eyesight typically fluctuates. Regular exams ensure that any necessary updates to prescriptions for eyeglasses or contact lenses are provided. Wearing an outdated prescription can strain the eyes and lead to headaches or blurred vision.
- Children: Often require more frequent checks due to rapid changes in their visual development.
- Adults: May experience subtle shifts over time; regular testing ensures proper correction.
- Seniors: Require close monitoring as aging eyes are prone to developing presbyopia and other degenerative conditions.
Overall Health Monitoring
Did you know that an eye exam can reveal signs of systemic health problems? The eyes provide a unique window into overall health since blood vessels, nerves, and tissues in the eyes reflect changes in the body.
Conditions That Can Be Detected:
| Condition | Signs Visible During an Eye Exam |
| Diabetes | Small hemorrhages or swelling in retinal blood vessels |
| High Blood Pressure | Narrowing or leakage of blood vessels |
| High Cholesterol | Yellowish deposits on the cornea |
| Autoimmune Diseases | Inflammation visible within different parts of the eye |
By identifying these signs early on, your optometrist or ophthalmologist may recommend further evaluation by your primary care physician.
Improved Quality of Life
Good vision is essential for performing everyday tasks such as reading, driving, working on computers, and engaging in hobbies. Undiagnosed vision problems can affect productivity and quality of life over time. Routine eye exams ensure that any impairments are diagnosed promptly so corrective measures can be taken to maintain clear vision.
Common Symptoms That Warrant an Immediate Exam
- Persistent headaches
- Blurred or double vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Difficulty focusing
Recommendations for Exam Frequency
| Age Group | Recommended Frequency |
| Children (3–5 yrs) | At least once during this period |
| Adults (18–39) | Every two years if no risk factors |
| Adults (40–64) | Every 1–2 years |
| Seniors (65+) | Annually |
Individuals with specific conditions like diabetes or a family history of glaucoma may need more frequent visits based on their doctor’s recommendations.
Regularly scheduled comprehensive eye exams are instrumental not only for maintaining optimal eyesight but also for promoting overall health awareness. Make it a priority to consult with a qualified eye care professional at intervals suitable for your needs.
Pediatric Eye Exams: Everything Parents Need to Know for Their Child’s Vision Care
Pediatric eye exams play a crucial role in ensuring your child’s visual health and overall development. Children rely heavily on their vision for learning, playing, and interacting with the world around them. As such, early detection of vision issues is essential for preventing long-term complications. This guide covers key aspects of pediatric eye exams that parents should know to safeguard their child’s vision.
Importance of Pediatric Eye Exams
Many childhood vision problems can go unnoticed because children may not realize they have a problem or may be unable to articulate it.
- Refractive errors: Conditions like nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism.
- Amblyopia (lazy eye): Reduced vision in one eye due to unequal focus or other issues.
- Strabismus (crossed eyes): Misalignment of the eyes that can affect depth perception.
- Eye health problems: Issues such as infections, allergies, or even rare conditions like pediatric glaucoma or cataracts.
Without proper intervention, these conditions could impact your child’s ability to learn and their overall quality of life.
Recommended Schedule for Pediatric Eye Exams
| Age Group | Recommended Exam Frequency |
| Newborn to 6 months | Vision screening during well-child visits by a pediatrician |
| 6 months to 1 year | Comprehensive eye exam by an optometrist or ophthalmologist if needed |
| 3 years | Comprehensive eye exam before preschool |
| 5 years and older | Annual exams during school years or as recommended by your doctor |
Parents should also seek an immediate evaluation if their child shows symptoms like difficulty focusing, squinting frequently, excessive tearing, or complaints about blurry vision.
What Happens During a Pediatric Eye Exam?
A pediatric eye exam is tailored to assess both the functional ability and overall health of a child’s eyes.
- Discussion about family history of eye conditions.
- Questions about any observed visual challenges in your child.
- Use of age-appropriate techniques like picture charts instead of letter-based Snellen charts.
- Assessment of near and distance vision clarity.
- Tests using light sources or toys to ensure both eyes are properly aligned.
- Determination if corrective lenses are required through tools like retinoscopes.
- Examination with specialized equipment like ophthalmoscopes.
- Identification of any structural abnormalities in the cornea, retina, or optic nerve.
Tips for Parents Preparing for Their Child’s Eye Exam
- Familiarize yourself with common tests so you can explain what’s happening.
- Schedule appointments when your child is most alert, such as mornings.
- Bring any necessary documents including medical history records.
- Encourage good behavior by framing the visit as an exciting experience rather than something stressful.
Regular pediatric eye exams are foundational steps toward protecting your child’s sight while supporting their cognitive development and learning potential. Being proactive ensures their best chance at maintaining clear vision throughout childhood and beyond.
Pediatric Eye Exams: Everything Parents Need to Know for Their Child’s Vision Care
Caring for a child’s vision is an essential part of their overall health and development. Pediatric eye exams are specifically designed to evaluate the unique needs of children’s eyes, ensuring they can see clearly and detect any potential issues early. Here’s everything parents need to know about pediatric eye care.
Why Are Pediatric Eye Exams Important?
Children rely on their vision to learn, play, and interact with the world around them. Vision problems can interfere with academic performance, social interaction, and even motor skill development. Early detection of eye issues allows for timely treatment, minimizing long-term effects on a child’s visual health.
Key reasons pediatric eye exams are critical include: – Early Detection of Conditions: Identifies issues such as amblyopia (lazy eye), strabismus (crossed eyes), or refractive errors (nearsightedness, farsightedness).Monitoring Development: Ensures proper alignment and focusing abilities as their eyes grow.Preventing Learning Difficulties: Many learning challenges stem from undiagnosed vision problems.
When Should Children Get an Eye Exam?
The American Optometric Association recommends the following schedule for children’s eye exams: | Age Range | Type of Exam | |—————————–|———————————————————| | 6 months | First comprehensive exam to check basic visual functions | | 3 years | Second exam to assess visual acuity and binocular vision | | Before starting school | Full exam to ensure readiness for academic activities | | Every one to two years | Regular follow-ups if no significant issues are detected |
Signs Your Child Might Need an Earlier Exam
Parents should schedule an appointment sooner if they notice: – Squinting or difficulty focusing on objects – Frequent rubbing of the eyes – Excessive tearing or redness – Complaints about headaches or blurry vision – Holding books or screens too close
What Happens During a Pediatric Eye Exam?
A pediatric eye exam is tailored for young patients using techniques that make the process comfortable and engaging.
- Health Evaluation: The doctor will review family history and discuss any symptoms your child might be experiencing.
- Visual Acuity Test: Uses age-appropriate charts or symbols to measure how well your child can see at various distances.
- Binocular Vision Testing: Assesses how well both eyes work together.
- Color Vision Screening: Determines color discrimination ability.
- Eye Alignment Check: Looks for signs of strabismus or other alignment issues.
- Pupil Responses & Eye Movement Tests: Evaluates neurological function related to vision.
Tips for Parents Preparing Their Child
For many children, a visit to the eye doctor might feel intimidating at first.
- Talk about what they can expect in simple terms.
- Bring along their favorite toy or book for comfort.
- Choose a time when your child is typically alert and rested.
- Encourage them by explaining how this helps them see better.
Regular pediatric eye exams play a vital role in protecting your child’s vision health as they grow. By staying proactive about scheduling appointments, parents can ensure their children have the best possible start in life with clear sight.
- Finding the Right Eye Clinic Houston TX: Understanding the Role of an Ophthalmologist Across All Ages
- 8 Essential Eye Tests Included in a Comprehensive Optometry Houston TX Exam
- How A Houston TX Eye Doctor Can Help You Maintain Healthy Vision With Regular Adult Eye Exams
- How to Choose the Right Houston TX Optometrist and Understand the Difference from an Ophthalmologist
- Choosing the Right Eye Doctor at an Eye Clinic Houston TX: Optometrist vs. Ophthalmologist
- The Importance of Visiting a Houston TX Eye Doctor for Comprehensive Eye Care as You Age